By Damon Smith
Rain, and the return of more humid weather, has meant that risk of tar spot of corn and white mold of soybean has increased over the past week. Now is the time to think about your in-season management plan for both of these diseases. Let’s dig in a bit on what the risk looks like for each disease.
Tar spot in Corn
This week we added Fond du Lac County to the tar spot map (Fig. 1). We also continue to see tar spot slowly increasing in plots and production fields on the Arlington research station. Looking back at our records from last season, we are tracking almost identically with what happened last year. I know folks think it is dry, but the tar spot fungus doesn’t care. It might move slow in these conditions, but the elevated humidity provides adequate leaf wetness for the disease to slowly progress. Should it start raining more regularly I expect the disease to pick up speed.
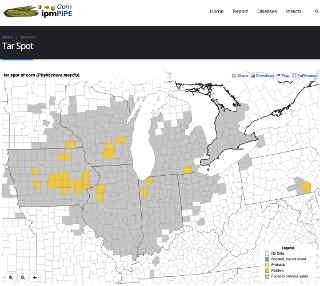
Fig 1. 7-22-22 reports https://corn.ipmpipe.org/tarspot/
Corn is rapidly approaching (if not already at) the optimal window of opportunity (VT-R3) for spraying fungicide to control tar spot. Given the high risk for tar spot across much of the state (Fig. 2), now is the time to call in that fungicide application if you are planning on it. Given the possible constraints on locating a custom applicator, getting the order in earlier than later may ensure application of fungicide by the R3 corn growth stage. Get out and scout, scout, scout!
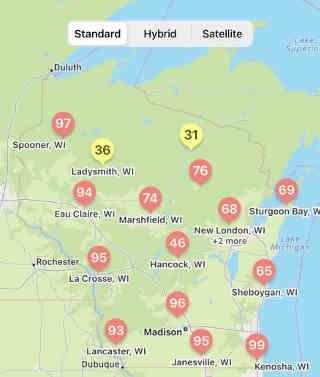
Fig 2. Tar Spot Risk for Wisconsin on July 21, 2022 as shown in smartphone app
White Mold of Soybean
White mold risk has increased from reasonably low last week, to mostly moderate across the state, this week (Fig. 3). Risk trends are also increasing, indicating that weather is continuing to become more favorable for white mold development. As we approach the R3 soybean growth stage, it will be important to make a decision on fungicide application, especially if you haven’t already applied a fungicide. If rain moves in over the next 7-10 days, expect risk to continue to increase. In irrigated fields we have been able to find apothecia (the mushroom-like structure that produces spores that infect soybean). This corroborates the increased risk we are seeing even in non-irrigated fields.
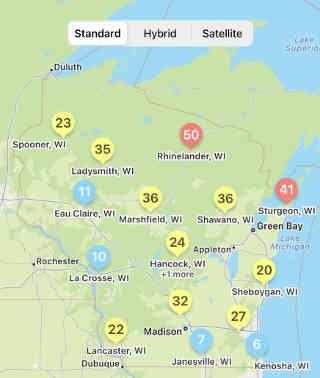
Fig 3. White mold risk in Wisconsin for July 21, 2022 as shown in smartphone app.
Source : wisc.edu